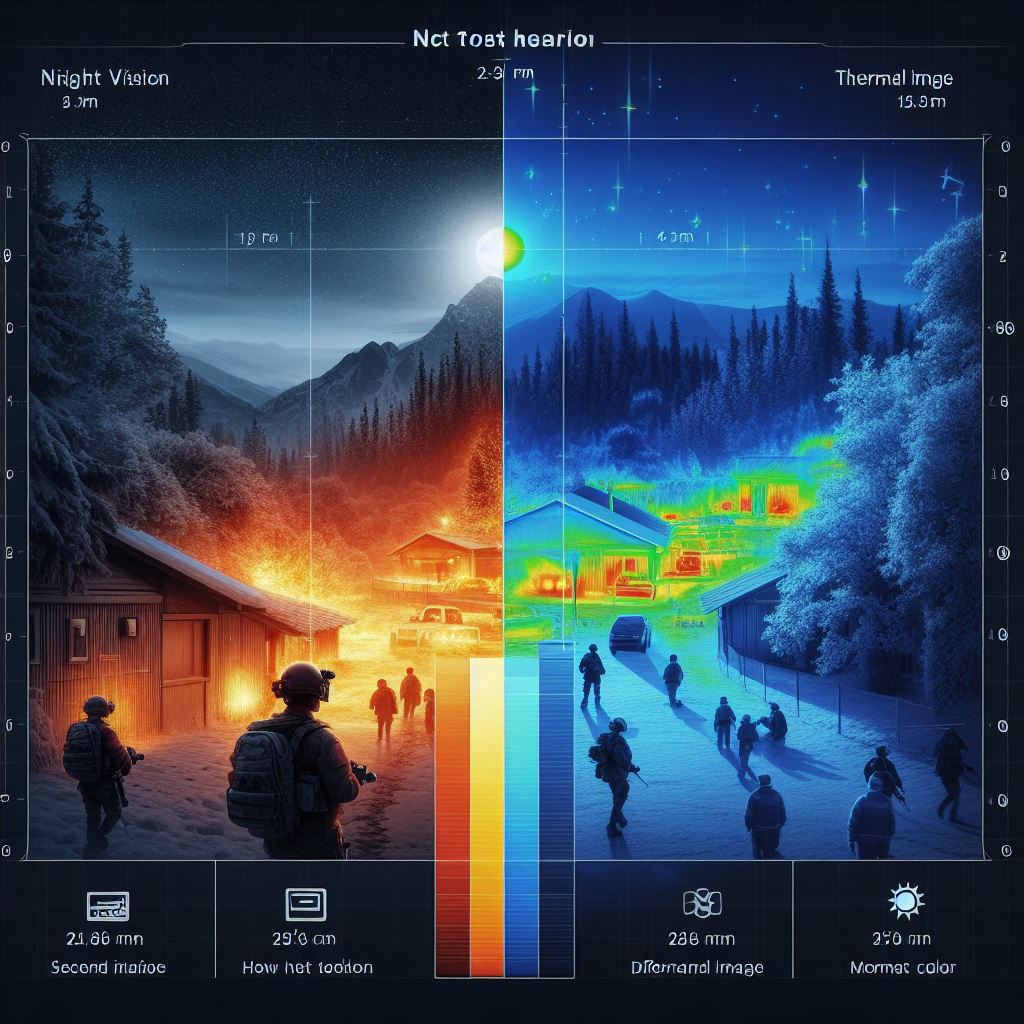
Understanding the Differences: Thermal Imaging vs. Night Vision
Thermal imaging and night vision are two technologies that are often used interchangeably, but they are actually quite different. While both technologies allow us to see in the dark, they do so in different ways and have different applications. Understanding the differences between thermal imaging and night vision is important for anyone who wants to make an informed decision about which technology to use.
Thermal imaging works by detecting the heat emitted by objects and converting it into a visible image. This technology is based on the principle that all objects emit infrared radiation, which is a form of heat. The hotter an object is, the more infrared radiation it emits. Thermal imaging cameras use special sensors that can detect this radiation and convert it into an image that we can see. The resulting image shows the variations in temperature of objects, with hotter objects appearing brighter and cooler objects appearing darker.
Night vision, on the other hand, works by amplifying the available light in the environment to make it visible to the human eye. Night vision devices use image intensifier tubes that capture the small amount of light present in the dark and amplify it to create a visible image. This technology is based on the fact that even in complete darkness, there is still some ambient light available, such as moonlight or starlight. Night vision devices can amplify this light by thousands of times, allowing us to see in the dark.
One of the main differences between thermal imaging and night vision is the way they perceive the environment. Thermal imaging relies on the heat emitted by objects, so it can detect objects even if they are not emitting any light. This makes thermal imaging particularly useful in situations where there is no ambient light, such as in complete darkness or in foggy conditions. Night vision, on the other hand, relies on the available light, so it requires at least some ambient light to work effectively. In situations where there is no ambient light, night vision devices may not be able to provide a clear image.
Another difference between thermal imaging and night vision is their range. Thermal imaging can detect objects at much longer distances than night vision. This is because thermal imaging is not dependent on the amount of available light, so it can detect objects that are far away. Night vision, on the other hand, is limited by the amount of available light, so its range is typically shorter than thermal imaging.
The applications of thermal imaging and night vision also differ. Thermal imaging is commonly used in military and law enforcement operations, as well as in search and rescue missions. It can be used to detect hidden objects, track individuals, and identify potential threats. Night vision, on the other hand, is commonly used in surveillance, hunting, and navigation. It allows users to see in the dark without the need for additional light sources.
In conclusion, while thermal imaging and night vision are both technologies that allow us to see in the dark, they are fundamentally different. Thermal imaging detects the heat emitted by objects, while night vision amplifies the available light. Thermal imaging can detect objects in complete darkness and has a longer range, while night vision requires some ambient light and has a shorter range. Understanding these differences is important for anyone who wants to choose the right technology for their specific needs.
Applications and Advantages of Thermal Imaging Technology
Thermal imaging technology has become increasingly popular in recent years, with applications ranging from military operations to medical diagnostics. However, there is often confusion about whether thermal imaging is the same as night vision. In this article, we will explore the applications and advantages of thermal imaging technology, and clarify the differences between thermal imaging and night vision.
One of the key applications of thermal imaging technology is in the field of law enforcement and military operations. Thermal imaging cameras can detect the heat signatures emitted by objects and individuals, allowing law enforcement officers and military personnel to identify potential threats even in complete darkness. This ability to see in the dark gives thermal imaging technology a distinct advantage over traditional night vision devices, which rely on amplifying available light.
Another important application of thermal imaging technology is in the field of building inspections. Thermal cameras can detect heat loss and identify areas of poor insulation, allowing homeowners and building inspectors to identify energy inefficiencies and make necessary repairs. This can result in significant cost savings by reducing energy consumption and improving overall building performance.
In the medical field, thermal imaging technology is used for a variety of purposes. For example, it can be used to detect and monitor inflammation in the body, as inflamed areas tend to emit more heat. This can be particularly useful in diagnosing conditions such as arthritis or identifying infections. Additionally, thermal imaging can be used to detect breast cancer by identifying areas of increased blood flow and heat in the breast tissue.
One of the key advantages of thermal imaging technology is its ability to provide real-time, non-contact temperature measurements. This can be particularly useful in industrial settings, where monitoring temperature is critical for ensuring the safety and efficiency of processes. For example, thermal imaging cameras can be used to detect overheating in electrical systems or identify hotspots in machinery, allowing for timely maintenance and preventing costly breakdowns.
Furthermore, thermal imaging technology has proven to be invaluable in search and rescue operations. In situations where visibility is limited, such as dense fog or smoke-filled environments, thermal cameras can help locate individuals by detecting their body heat. This can significantly improve the chances of finding and rescuing people in emergency situations.
While thermal imaging technology offers many advantages, it is important to note that it is not the same as night vision. Night vision devices rely on amplifying available light, allowing the user to see in low-light conditions. In contrast, thermal imaging technology detects the heat emitted by objects and individuals, allowing for visibility in complete darkness. Both technologies have their own unique applications and advantages, and the choice between them depends on the specific needs of the user.
In conclusion, thermal imaging technology has a wide range of applications and advantages. From law enforcement and military operations to medical diagnostics and building inspections, thermal imaging cameras provide valuable insights and capabilities. While thermal imaging is not the same as night vision, it offers distinct advantages in terms of its ability to detect heat signatures and provide real-time temperature measurements. As technology continues to advance, the potential applications of thermal imaging are only expected to grow.
Exploring the Limitations of Night Vision Systems
Thermal imaging and night vision are two commonly used technologies that allow individuals to see in low-light or dark environments. While they serve a similar purpose, there are distinct differences between the two. This article aims to explore the limitations of night vision systems and clarify whether thermal imaging is the same as night vision.
Night vision systems rely on the amplification of available light to enhance visibility in dark conditions. They work by capturing the small amount of light present in the environment and amplifying it to create a visible image. This technology is commonly used in military operations, surveillance, and even in consumer products such as night vision goggles.
However, night vision systems have limitations. One of the main drawbacks is their dependence on ambient light. In situations where there is no available light, night vision devices become ineffective. This means that in complete darkness, night vision systems are unable to provide any visual information. Additionally, night vision can be easily affected by bright light sources, such as headlights or flashlights, which can cause temporary blindness or damage to the device.
On the other hand, thermal imaging operates based on the detection of heat signatures emitted by objects and living beings. It does not rely on ambient light, making it effective in complete darkness. Thermal imaging cameras detect the differences in temperature between objects and convert them into a visible image, where warmer objects appear brighter and cooler objects appear darker. This technology is widely used in various fields, including search and rescue operations, firefighting, and even medical diagnostics.
While thermal imaging can be highly effective in detecting heat signatures, it also has its limitations. One of the main drawbacks is its inability to provide detailed visual information. Thermal images are often presented in grayscale, lacking the color and fine details that can be seen with night vision systems. This can make it challenging to identify specific objects or individuals in certain situations.
Another limitation of thermal imaging is its inability to see through certain materials. For example, glass and other transparent surfaces can block thermal radiation, making it difficult to detect objects behind them. This can be a significant disadvantage in scenarios where visibility through barriers is crucial.
In conclusion, thermal imaging and night vision are distinct technologies with their own limitations. While night vision systems rely on amplifying available light and can be affected by bright light sources, thermal imaging operates based on detecting heat signatures and is effective in complete darkness. However, thermal imaging lacks the detailed visual information provided by night vision systems and can be hindered by certain materials. Therefore, it is clear that thermal imaging is not the same as night vision, and each technology has its own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these limitations is crucial in choosing the appropriate technology for specific applications.
Choosing the Right Imaging Technology: Factors to Consider
Thermal imaging and night vision are two distinct imaging technologies that serve different purposes. While they both enable vision in low-light conditions, they operate on different principles and have varying applications. Understanding the differences between these technologies is crucial when choosing the right imaging technology for specific needs.
Thermal imaging, also known as infrared imaging, relies on detecting the heat emitted by objects and converting it into a visible image. This technology is based on the principle that all objects emit infrared radiation, which is invisible to the human eye. By capturing this radiation and converting it into a visible image, thermal cameras can create a detailed representation of the heat patterns in a scene. This makes thermal imaging particularly useful for detecting temperature differences and identifying objects based on their heat signatures.
On the other hand, night vision technology amplifies the available light in a scene to enhance visibility in low-light conditions. Night vision devices work by collecting and intensifying the ambient light, such as moonlight or starlight, and then projecting it onto a screen or eyepiece. This allows the viewer to see objects that would otherwise be invisible to the naked eye in darkness. Night vision technology is commonly used in military operations, surveillance, and wildlife observation.
While both thermal imaging and night vision enable vision in low-light conditions, they have distinct advantages and limitations. Thermal imaging is particularly effective in complete darkness or situations where there is no ambient light available. It can detect heat signatures through smoke, fog, and other obscurants, making it valuable in firefighting, search and rescue operations, and industrial inspections. However, thermal imaging has limitations when it comes to identifying fine details or distinguishing between objects with similar heat signatures.
Night vision, on the other hand, relies on existing ambient light and is most effective in situations where there is some level of illumination, such as moonlight or streetlights. It provides a more detailed and recognizable image of the scene, allowing for better identification of objects and people. However, night vision devices may struggle in complete darkness or when there is no available ambient light.
When choosing the right imaging technology, several factors need to be considered. The intended application and environmental conditions play a crucial role in determining which technology is most suitable. If the goal is to detect temperature differences or identify objects based on their heat signatures, thermal imaging is the preferred choice. On the other hand, if the objective is to enhance visibility in low-light conditions where some ambient light is available, night vision technology is more appropriate.
Additionally, budget constraints and operational requirements should also be taken into account. Thermal imaging technology tends to be more expensive than night vision, making it less accessible for some applications. Night vision devices, on the other hand, are more widely available and come in various forms, including binoculars, goggles, and scopes.
In conclusion, thermal imaging and night vision are distinct imaging technologies that serve different purposes. While both enable vision in low-light conditions, thermal imaging relies on detecting heat signatures, while night vision amplifies existing ambient light. Understanding the differences between these technologies and considering factors such as the intended application, environmental conditions, budget, and operational requirements is crucial when choosing the right imaging technology. By carefully evaluating these factors, one can make an informed decision and select the most suitable technology for their specific needs.